How to Find the Area of a Rectangle: Proven Methods and Techniques
Understanding the Rectangle Area Formula
To accurately determine the area of a rectangle, one must use the **rectangle area formula**: Area = Length × Width. This basic geometry formula forms the foundation for calculating the area of rectangular shapes in various applications. A rectangle consists of two primary dimensions: length and width. The length is usually the longer side, while the width is the shorter side. **Calculating the area** using this straightforward formula is essential for various practical applications, such as estimating materials needed for construction, landscaping, or even crafting. In real-life scenarios, understanding the **dimensions of a rectangle** is crucial for making effective calculations. For example, if you have a rectangle that is 10 meters long and 5 meters wide, the area would be 50 square meters, making it easier to visualize how much space it occupies.
Essential Properties of Rectangles
Rectangles share specific geometric properties that help in understanding their area calculation. Each rectangle contains four right angles and opposite sides that are equal in length. One useful property related to area is the **length-width ratio**, which can be essential for tasks like design and architecture. This ratio influences both aesthetic appeal and practical utility when determining areas in real-world applications. Furthermore, recognizing these properties allows for better understanding when working with **area calculation steps** involved in more complex geometric shapes. For instance, ensuring correct angle measurements is fundamental for not only rectangles but also shapes that may encompass them.
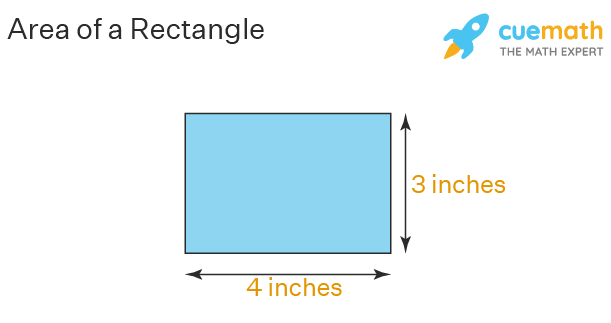
Visual Examples of Rectangle Area Calculation
Visualizing area calculations aids in better comprehension, particularly when learning area concepts. By sketching rectangles or utilizing digital tools, you can clearly see how changing length and width affects the area. For example, editing the length from 5 to 7 units while keeping width constant can demonstrate how the area expands from 35 to 49 square units. Utilizing techniques such as drawing grids or employing area measurement tools can solidify these concepts in educational settings. When teaching rectangle area calculations, practical examples highlighting how these formulas apply in everyday life can significantly enhance students’ understanding.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Area
When you need to **calculate the rectangle area**, following a structured approach can simplify the process. Start by measuring the **length and width** of the rectangle. To achieve accurate results, ensure you use the same unit of measurement for both dimensions, whether meters, feet, or inches. Next, multiply these two measurements using the formula (Area = Length × Width). Lastly, write down the result with proper units—always expressing the area in square units. This methodical technique can be invaluable when introducing students to area measurement.
Real-World Applications of Area Calculation
Understanding how to find the area of a rectangle has numerous **real-life applications**. In construction, calculating the area is essential for determining how much flooring, painting, or landscaping materials are needed. **Area problems** frequently appear in business scenarios where space utilization must be optimized, and accurate area measurements are crucial for site assessments. Additionally, in agricultural practices, calculating plot sizes accurately can significantly impact operational efficiency. This skill extends beyond academic environments, making it valuable in various professional and personal contexts.
Common Mistakes in Area Calculation
While straightforward, area calculations can sometimes lead to misunderstandings. A common mistake is failing to use consistent units, thus impacting the overall results. For example, if you measure length in meters and width in centimeters without conversion, the area will be incorrect. Additionally, mislabeling dimensions when working with **rectangle examples** can mislead individuals unfamiliar with proper area calculation techniques. Careful attention to these details is paramount in ensuring precision in all area measurement activities.
Advanced Techniques for Area Calculation
As you delve deeper into understanding the area of simple shapes, employing advanced area calculation techniques can help address complex geometry problems. Techniques such as breaking down irregular shapes into multiple rectangles or applying geometric formulas for **area calculations** can enhance one’s analytical skills, vital for tasks in various fields. This approach allows for a nuanced understanding of how different dimensions impact area.
Comparing Areas: Rectangle vs. Other Shapes
An essential aspect of mastering area calculations involves **comparing area sizes** between different shapes. Understanding how the area of rectangles relates to other polygons allows for deeper insights into geometric properties. By analyzing how different shapes such as triangles and circles cover areas, one can apply similar principles to fostering more robust problem-solving strategies. For example, comparing a square’s area, which is a specific type of rectangle, can illustrate broader concepts in geometry.
Tools and Resources for Enhanced Learning
Many resources are available for enhancing your understanding and practice in area calculations. Educational platforms often provide interactive geometry tools to visualize **area principles** effectively. Additionally, various mobile applications can simplify area calculations and facilitate practical learning. Engaging with such tools can augment traditional learning methodologies, especially for students struggling with geometric concepts. A well-documented guide can lead to long-lasting retention of geometrical measures like the area, shaping a holistic understanding of its applications.
Key Takeaways
- The area of a rectangle is calculated using the formula: Area = Length × Width.
- Understanding the properties and dimensions of a rectangle aids in practical area measurement.
- Utilizing a structured approach enhances the learning experience when performing area calculations.
- Real-world applications make learning the area of rectangles relevant and necessary.
- Using advanced techniques for area calculation can simplify solving complex geometric problems.
FAQ
1. What is the rectangle area formula, and how is it used?
The rectangle area formula, Area = Length × Width, is utilized to calculate the space a rectangle occupies. This straightforward formula multiplies the rectangle’s two dimensions, serving various practical applications in construction, design, and landscaping.
2. How do I measure the dimensions of a rectangle accurately?
To determine the dimensions of a rectangle accurately, use a ruler or measuring tape to measure the length and width in the same unit. Ensure that measurements are precise, as any discrepancies can lead to incorrect area calculations.
3. Why is it crucial to maintain consistent units in area calculations?
Maintaining consistent units is vital to produce accurate area calculations. Using different measurement units for length and width without conversion may yield erroneous results. Always convert measurements to the same unit before applying them to the area formula.
4. Can the area of a rectangle be applied in real life?
Absolutely! The area of a rectangle finds applications in real life, like planning layouts for construction projects, designing landscaping, or measuring furniture space in residences. Understanding the rectangle’s area is practical and beneficial across diverse fields.
5. What are common mistakes made when calculating rectangle areas?
Common mistakes include using inconsistent measurement units, mislabeling dimensions, or misapplication of the area formula itself. Being mindful of these errors can help ensure more precise area calculations, especially in educational or professional contexts.
6. What other shapes can be compared using area calculations?
Area calculations can also apply to shapes such as triangles, circles, and polygons. By comparing these areas, one can understand fundamental geometric relationships and principles, enhancing the overall skill set in geometry content.
7. Are there any tools available to assist with area calculations?
Yes, many online calculators and educational resources are available to help with area calculations. These include apps for mobile devices and interactive platforms that demonstrate geometric areas dynamically. Utilizing technology can significantly enhance the learning experience.