“`html
Effective Ways to Find Interquartile Range for Accurate Data Analysis
The interquartile range, often abbreviated as IQR, is a fundamental statistical measure that provides insight into the spread of data. It specifically represents the range of the middle 50% of a data set, making it a valuable tool in data analysis. Calculating the IQR helps statisticians understand data dispersion, variability in data, and identify potential outliers that may skew results. In this article, we will discuss effective methods for finding IQR, including its quartile calculation, and explore its importance in descriptive statistics.
Understanding Quartiles and Their Importance
Quartiles are values in a data set that divide the data into four equal parts. The first quartile (Q1) represents the 25th percentile, while the third quartile (Q3) signifies the 75th percentile. The IQR is then computed as the difference between these two quartiles, providing an effective measure of statistical dispersion. Understanding quartiles allows analysts to summarize data effectively, which is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions from data sets.
What are Quartiles?
To illustrate the concept, consider a sorted dataset: [3, 7, 8, 12, 20]. The first quartile, Q1, is the median of the first half of the data, while Q3 is the median of the second half. Using this method ensures that you can effectively analyze the spread of data and interpret the underlying trends.
Calculating Quartile Values
To find the quartile values, you can either manually calculate them or use statistical software. The manual method involves first ordering your data, finding the medians for each half (Q1 and Q3), and ultimately deriving the IQR through the equation: IQR = Q3 – Q1. Using tools like R or Python can simplify these calculations significantly, especially with larger datasets.
Steps to Calculate the Interquartile Range
Calculating the IQR consists of a two-step process that ensures accurate results. This method is fundamental for robust data analysis and helps in data interpretation.
Step 1: Organize Your Data
First, start by organizing your data set in ascending order. For instance, a data set like [2, 5, 8, 12, 15, 19] should be appropriately sorted before analysis. Organizing data as its first step ensures accurate and reliable quartile calculation, forming a strong foundation for the IQR calculation.
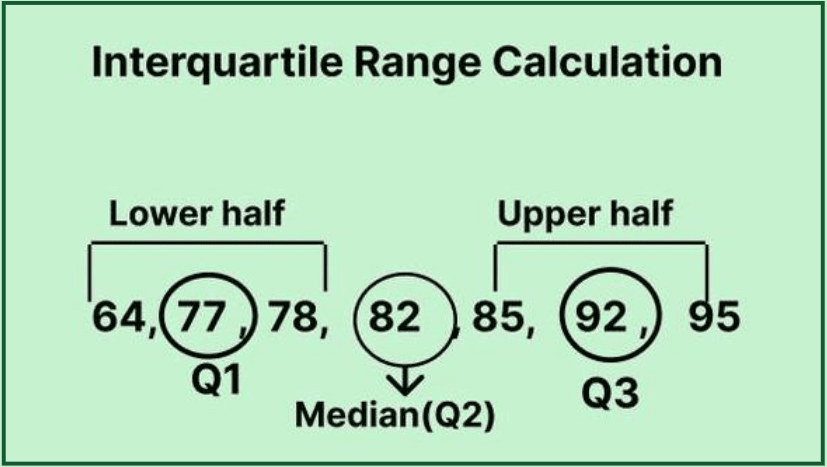
Step 2: Identify Q1 and Q3
Next, you’ll want to identify Q1 and Q3. For the given data set, Q1 is calculated by finding the median of the first half and Q3 by determining the median of the second half. In our example, if Q1 = 5 and Q3 = 15, the IQR would be calculated as IQR = Q3 – Q1 = 15 – 5 = 10. This process emphasizes the key aspects of data organization within statistical calculations.
Visualizing the Interquartile Range
A box plot is an effective way to visualize the IQR alongside other quartile-related measures. This graphical representation highlights Q1, Q2 (the median), Q3, as well as potential outliers. Understanding how to create box plots can significantly enhance your data analysis techniques.
Creating a Box Plot
To create a box plot, follow these steps: draw a box from Q1 to Q3, add a line at the median (Q2), and extend whiskers to the minimum and maximum data values within 1.5 times the IQR. Any data points outside this range are typically considered outliers. This visual representation aids in interpreting the distribution and comparing different datasets.
Using IQR for Outlier Detection
Another significant benefit of calculating the IQR is its utility in outlier detection. By leveraging the IQR, you can identify outliers through the method of fences: values below Q1 – 1.5 * IQR or above Q3 + 1.5 * IQR are potential outliers. This procedure can streamline data examination and enhance the quality of analyses, ensuring statistical integrity in your results.
Implications of IQR in Data Analysis
The IQR is not just a number; it plays a critical role in understanding the variability in data and is a vital component of descriptive statistics. It emphasizes the range in which the central 50% of the data falls, allowing for a clearer understanding of data distribution.
Variance and Standard Deviation in Context
While the IQR provides crucial insights into range of data, other measures like variance and standard deviation also contribute to understanding statistical dispersion. These statistics can complement the IQR for a comprehensive analysis, balancing out biases and variances in datasets.
Using the IQR in Data Reporting
In data reporting, presenting the IQR alongside median and mean values helps provide a more accurate portrayal of data. Effective reporting includes a combination of measures to articulate findings clearly, thus enhancing the interpretability of results in research or analysis settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding the interquartile range is an indispensable skill in data analysis. This crucial measure serves as a foundation for understanding the spread of data and analyzing datasets more effectively. By implementing the techniques discussed, including proper quartile calculation and visual representation through box plots, you can bolster your skills in statistical analysis.
FAQ
1. What are data sets commonly used in IQR calculation?
A common dataset for calculating IQR includes responses from surveys, scores from tests, or any numerical data analyzed statistically. Understanding the importance of selecting relatable data collections enhances the relevance of your analysis.
2. How do I calculate quartiles in Python?
In Python, quartiles can be calculated using libraries such as NumPy. By simply using the function numpy.percentile(data, [25, 75]), you can retrieve Q1 and Q3 swiftly.
3. What is the difference between IQR and standard deviation?
The IQR focuses specifically on the middle 50% of the data, whereas standard deviation measures the average distance of data points from the mean. Both are critical in portraying different facets of data distribution.
4. Why is the IQR important in data analysis?
The IQR is critical because it effectively communicates data spread, reduces the influence of potential outliers, and assists in better data interpretation, ultimately contributing to a more robust analysis.
5. How do I visualize the IQR in a dataset?
The IQR can be visualized using box plots. This representation aids in quickly understanding the range and distribution of a dataset, making outlier identification simple and effective.
6. Does the IQR vary between different data distributions?
Yes, the IQR can vary significantly across distributions. Generally, it’s higher in distributions with wider spreads compared to those with tighter clusters, making it a reliable measure of dispersion.
7. Can IQR be used with qualitative data?
No, the IQR is primarily applicable to quantitative data. Qualitative data requires different analytical approaches, as measures of central tendency may be unsuitable for categorical responses.
“`