Smart Ways to Find Vertical Asymptotes in 2025: Essential Techniques to Master Calculus!
Understanding Vertical Asymptotes: Definition and Basics
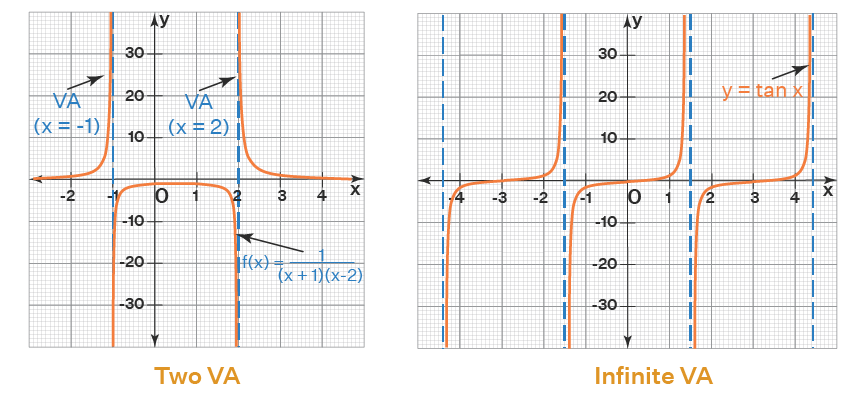
In calculus, **vertical asymptotes** are crucial in analyzing the behavior of functions. They occur where a function approaches infinity or negative infinity as the input approaches a specific value. Understanding the **vertical asymptote definition** is essential, as they indicate points of **discontinuity** in the graph of a function. This is particularly prevalent in **rational functions**, where vertical asymptotes often arise from undefined values in the denominator. Recognizing where these asymptotes lie enables you to predict the behavior of the function nearby, which is fundamental in graphing and analyzing mathematical functions.
Identifying Vertical Asymptotes in Rational Functions
To find **vertical asymptotes**, especially in **rational functions**, begin with the function written in a fraction form, where one polynomial is divided by another. The primary technique for **identifying vertical asymptotes** involves pinpointing values that make the denominator zero while the numerator is not zero. These undefined points often lead to **asymptotic behavior**. For instance, consider the function f(x) = (2x)/(x^2 – 9). Here, you can calculate the vertical asymptotes by setting the denominator x^2 – 9 = 0. Solving this gives x = 3 and x = -3, indicating that these values lead to **vertical asymptotes**.
Calculating and Sketching Graphs with Vertical Asymptotes
Once vertical asymptotes are determined, the next step is sketching the function and applying techniques to understand the **vertical behavior** near these asymptotes. This is where **graphing techniques** come into play. Through the limits approaching the vertical asymptote values from both sides—left and right—you can analyze whether the function tends either towards positive or negative infinity. For f(x) = (2x)/(x^2 – 9), as x approaches 3 from the left, f(x) approaches positive infinity, and from the right, f(x) approaches negative infinity. This tells us that the curve will **trend upwards** on the left and downwards on the right of the asymptote at x = 3.
Advanced Techniques for Finding Vertical Asymptotes
As you delve deeper into calculus, it becomes essential to master advanced techniques for finding vertical asymptotes. Mastering these methods inclines students towards **asymptotic analysis** and greater understanding of **function behavior**.
Vertical Asymptotes in Polynomial Functions
While rational functions are prevalent, it’s important to determine the vertical asymptotes in **polynomial functions**. Although polynomial equations generally exhibit continuity across their defined range, certain manipulations can introduce discontinuities. For instance, dividing a polynomial can create **vertical asymptotes** depending on how many times the polynomial intersects the x-axis. Understanding these intersections enhances your ability to analyze and sketch graphs where **vertical asymptotes** may exist.
Vertical Asymptotes versus Horizontal Asymptotes
Importantly, **vertical asymptotes** signify a fundamentally different behavior than **horizontal asymptotes**. While vertical asymptotes indicate undefined behavior at specific x-values, horizontal asymptotes address the behavior of the function as x approaches infinity. Recognizing this difference is vital in calculus, as it will influence both function graphing and limits evaluation. By fulfilling both criteria, you can create comprehensive and representative graphs of functions, ensuring clear identification between various types of asymptotic behavior.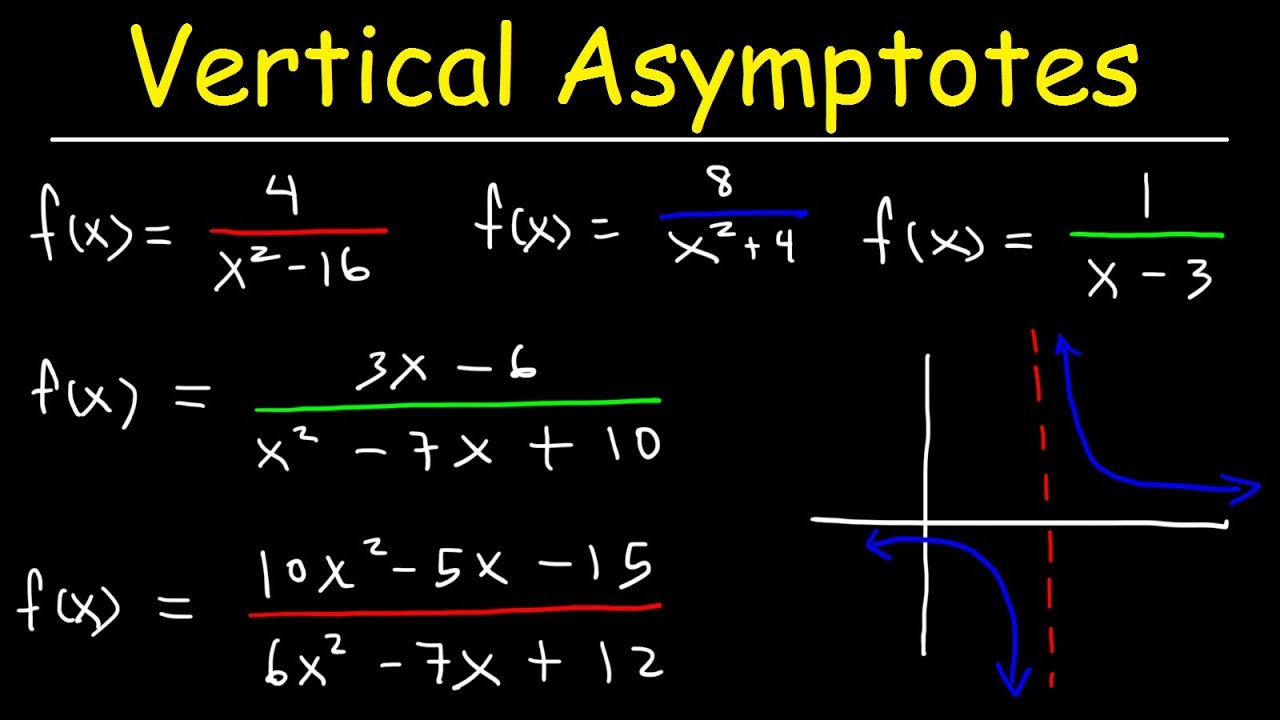
Practical Applications of Vertical Asymptotes
Understanding and finding **vertical asymptotes** is not only essential in theoretical calculus but also has numerous **real-world applications**. From engineering to economics, the idea of function limits—and hence vertical asymptotes—comes into play regularly.
Vertical Asymptotes in Real-World Scenarios
In fields such as physics, certain equations describe phenomena that can become undefined under conditions modeled by vertical asymptotes. Understanding these situations allows for optimal decision-making. For example, in metrics involving velocity and time, recognizing the point where the height may lead to undefined velocity allows for practical safety measures. Here, vertical asymptotes tell you critical stopping conditions to avoid accidents. These insights showcase how analyzing discontinuities can save time, resources, and even lives.
Challenges in Identifying Vertical Asymptotes
Students often face **challenges** in identifying vertical asymptotes due to common misconceptions about limits. A frequent error arises in miscalculating when both numerator and denominator equal zero simultaneously; this indicates a possibly removable discontinuity rather than an asymptote. Therefore, employing a methodical approach is vital in function analysis, specifically recognizing when to apply simplification or factoring to gain better insights into discontinuities. Employing a vertical asymptotes checklist can guide you through these traps, ensuring accurate identification of asymptotes in varied situations.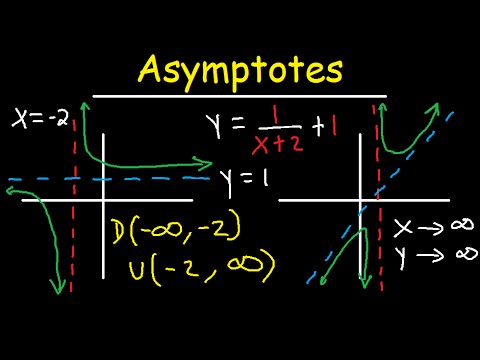
Key Takeaways
- Vertical asymptotes signify undefined behavior of functions built into rational functions, identified quickly through limit evaluation.
- These asymptotes can be profound indicators of various mathematical phenomena, extending to real-world applications.
- Recognizing the difference between vertical and horizontal asymptotes enhances overall function comprehension and analytical capabilities.
- Having a vertical asymptotes checklist aids in effectively identifying asymptotic behavior, reducing common calculative errors.
FAQ
1. What are vertical asymptotes in calculus?
Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines that represent the input values where a function’s output approaches infinity or negative infinity, typically occurring where the denominator of a rational function is zero. Understanding vertical asymptotes emphasizes the locations of discontinuities within the graph of a function.
2. How do I find vertical asymptotes in a rational function?
To **find vertical asymptotes** in a rational function, set the denominator equal to zero and solve for x. Any x-value that results in an undefined function while having a defined numerator alongside it will indicate a vertical asymptote.
3. Can vertical asymptotes occur in polynomial functions?
Generally, vertical asymptotes do not exist in **polynomial functions** because they are continuous across their domains. However, if you manipulate a polynomial, such as dividing it by another polynomial, vertical asymptotes can arise in the resulting functions if they lead to undefined values.
4. Why are limits important in understanding vertical asymptotes?
Limits highlight the behavior of functions as they approach vertical asymptotes, allowing you to analyze how values behave before reaching points of discontinuity. They provide insight into whether the function increases or decreases steeply near these asymptotic lines.
5. How can I avoid mistakes when identifying vertical asymptotes?
Avoid miscalculating vertical asymptotes by confirming that the numerator is not undefined when determining asymptotes through zero values of the denominator. Using a checklist dedicated to vertical asymptotes can help traversing past common misunderstandings and ensure the accurate identification of the behavior of functions.