How to Effectively Calculate Percent Error for Accurate Results in 2025
Understanding how to calculate percent error is crucial in fields ranging from science to engineering. Percent error calculation helps quantify the accuracy of experimental or measured values in relation to their real or accepted values. This article will delve into the formulas, practical examples, and significance of percent error, equipping you with the knowledge to assess accuracy effectively.
The Formula for Percent Error: Understanding the Basics
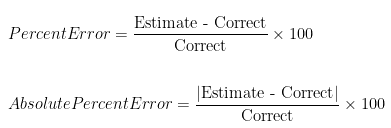
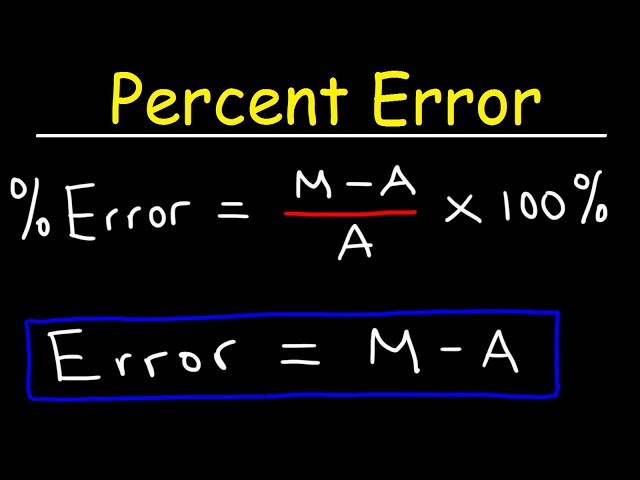
The formula for percent error serves as the foundation for analyzing the accuracy of measurements in various experimental activities. To calculate percent error, you can use the following formula:
Percent Error = (|Estimated Value – Actual Value| / |Actual Value|) × 100%
In this equation, the absolute difference between the estimated and actual values is divided by the actual value, and the result is multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage. For instance, if an experiment measures an object to be 98 grams, while its known weight is 100 grams, the percent error can be calculated as follows:
Percent Error = (|98 – 100| / |100|) × 100 = 2%
This calculation is particularly important in fields such as physics and chemistry, where accuracy can significantly impact research findings. By mastering this percentage error calculation process, researchers can ensure more reliable results in their experiments.
Examples of Percent Error in Different Fields
To further illustrate the concept of percent error, let’s look at a few examples across various disciplines. In chemistry, when calculating the concentration of a solution using a titration method, if the theoretical concentration was 0.50 M and the measured concentration was 0.48 M, the percent error would be analyzed as follows:
Percent Error = (|0.48 – 0.50| / |0.50|) × 100 = 4%
This small error percentage indicates a relatively accurate measurement, but it’s still essential to be aware of potential variations in experiments. In engineering, evaluating the percent error in predicting the lifecycle of materials can lead to better decision-making in design and construction processes. Understanding the impact of a low percent error helps engineers assess reliability in harsh conditions and improving structures accordingly.
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Percent Error
Many people often confuse percent error with absolute error or relative error, leading to misunderstandings in data interpretation. Absolute error is simply the magnitude of the difference between the measured and true values, without considering the significance of that difference. In contrast, relative error compares the absolute error to the actual value.
The significance of understanding these terms lies not only in your ability to calculate but also how you interpret the results. In statistical analysis of percent error, one might consider how it affects large datasets and the validity of conclusions drawn in research or experiments.
Practical Applications of Percent Error
The application of percent error extends beyond laboratories into real-world scenarios. For example, in quality control processes, companies often use percent error to determine whether their products meet specified standards. By consistently evaluating the importance of percent error in their manufacturing processes, businesses can enhance product accuracy and customer satisfaction.
Reducing Percent Error: Strategies for Improvement
To achieve better accuracy in measurements, implementing strategies to reduce percent error is essential. Here are a few tips:
- Ensure that equipment is properly calibrated, as inaccuracies in measurements often arise from miscalibrated instruments.
- Carry out multiple trials to account for variations in results. Calculating averages and applying the standard deviation can help minimize discrepancies.
- Take into consideration environmental factors that could impact measurements, such as temperature variations and human precision.
By applying these strategies, researchers and practitioners across domains can strive for results that approach the actual values in their respective studies.
Comparing Values with Percent Error in Research
When conducting research, using percent error in measurements allows for a standardized method to compare different values or methodologies. For example, in clinical trials, evaluating the effectiveness of various treatment dosages can depend on the variance suggested by percent error. A low percent error across different trials may indicate a reliable treatment that consistently produces expected results.
Understanding the Significance of Percent Error
In scientific experiments, percent error holds significant importance as it indicates the precision of data collection. Keeping track of percent error can help in making informed decisions related to experimental designs and protocols. High percent errors can reveal limitations in methods or equipment, prompting further inquiry into improvement measures. Particularly, assessing measurement error is essential in statistics, where understanding variability leads to better predictions and accuracy in data analysis.
Implementation of Standard Procedures for Accurate Percent Error Calculation
To ensure reliable outcomes, having a standardized procedure for calculating percent error can benefit researchers greatly. This involves setting clear criteria for acceptable error percentages based on historical data, guiding practitioners in determining acceptable limits for measurements. In educational settings, educators can also guide students in understanding and applying these standardized methods effectively when conducting experiments.
Evaluating and Interpreting Percent Error Results
To successfully utilize percent error in practical applications, it is crucial to critically evaluate the results. Understanding the context and conditions under which errors occur can provide insights into improvements. Interpretation of the results helps researchers identify key patterns or discrepancies in their data, serving as a foundation for honing related methodologies. Additionally, education or workshops on proper error handling fosters a culture of precision in scientific inquiry.
Key Takeaways
- Percent error calculation allows for quantifying the accuracy of measurements.
- Standardized formulas should be applied for clarity in results.
- Reducing percent error involves proper calibration, multiple trials, and consideration of environmental factors.
- Understanding the significance of percent error can aid in enhancing research quality.
FAQ
1. What is percent error definition?
Percent error is a way to quantify how far an estimated or measured value is from its actual value expressed as a percentage. It allows for a standardized method to evaluate and communicate the accuracy of measurements in a variety of fields.
2. How do you find percent error in experimental data?
To find percent error, subtract the actual value from the estimated value, take the absolute value of that difference, divide by the actual value, and multiply by 100. This gives a clear indication of accuracy in experimental data reporting.
3. What is the significance of low percent error?
A low percent error indicates high accuracy and reliability of the measurements. It provides confidence to researchers and practitioners that their data aligns closely with actual values, leading to more dependable conclusions in scientific studies.
4. How can I minimize percent error in measurements?
To minimize percent error, ensure accurate calibrations of measurement devices, conduct multiple trials for average results, and control for environmental influences that might affect results adversely, leading to inaccurate readings.
5. What is the difference between absolute and relative percent error?
Absolute error is the difference between the measured value and the actual value, while relative error is that difference divided by the actual value. Percent error usually represents relative error, standardized as a percentage for easier comprehension.