How to Properly Find the Y-Intercept: Essential Methods for 2025
The **y-intercept** is a fundamental concept in algebra and coordinate geometry, marking the point where a line intersects the y-axis. It is essential for graphing linear equations and understanding the behavior of functions. In this article, we’ll explore various methods to find the **y intercept**, delve into its significance, and provide practical tips for accurately calculating and interpreting it within mathematical modeling and real-life applications.
Understanding the Y-Intercept
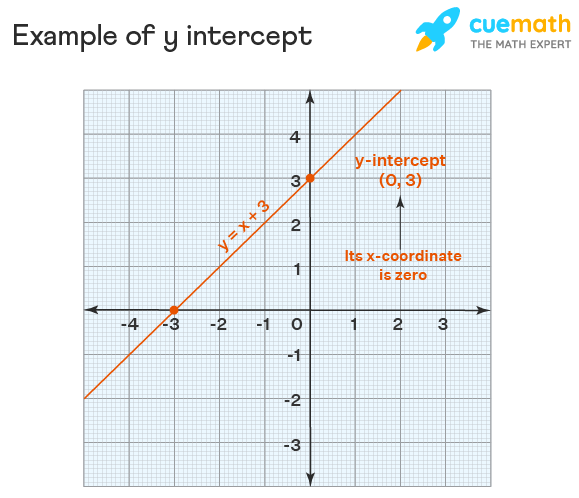
Before diving into how to **find the y intercept**, it is crucial to grasp its definition. Simply put, the **y intercept** is the value of y when x equals zero in a given equation—indicating where the graph intersects the y-axis. This intersection is vital in **linear relationships**, allowing for easier visualization of equations. The **y intercept formula** can be derived from the slope-intercept form of a line, denoted as y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b is the y-intercept.
Y-Intercept Definition
The **y intercept definition** encapsulates the core principle of where a graph crosses the y-axis. When plotting a function, identifying the **y intercept** helps in understanding the starting point of the graph. For instance, in the equation y = 3x + 4, substituting x = 0 gives y = 4, meaning the graph intersects the y-axis at (0,4).
Significance of the Y-Intercept
The **significance of the y intercept** extends beyond simple graphical representation. It serves as a metric for evaluating the function’s output at a specific input, providing insights into its behavior under various conditions. The **intercepts of a function**—both y and x—can help reveal the function’s trends, potential maximum or minimum values, and essential characteristics such as symmetry.
Examples of Y Intercept Calculation
To cement our understanding of how to **calculate the y intercept**, let’s analyze a few examples. Consider the linear equation y = -2x + 5. Here, by setting x = 0, we calculate y = 5, revealing that the y-intercept is at the point (0,5). On the graph, this point would be marked clearly, serving as a reference for how changes in x affect y as the line ascends or descends.
Methods to Find the Y-Intercept
When managing algebraic expressions or **linear equations**, numerous methods exist to **find the y intercept**. Whether you’re utilizing algebraic manipulation or graphical representations, knowing effective strategies is essential for accuracy. The **slope-intercept form** is widely regarded as the most straightforward method for determining the y-intercept.
Using the Slope-Intercept Form
As previously mentioned, the **slope-intercept form** of a line, y = mx + b, provides an efficient means for finding the **y intercept**. In this format, the y-intercept is simply the constant term, b. For example, in the equation y = 4x - 3, the y-intercept is -3. This method is favored for its directness and is particularly suited for **math problems** where rapid visualization is required.
Graphical Representation
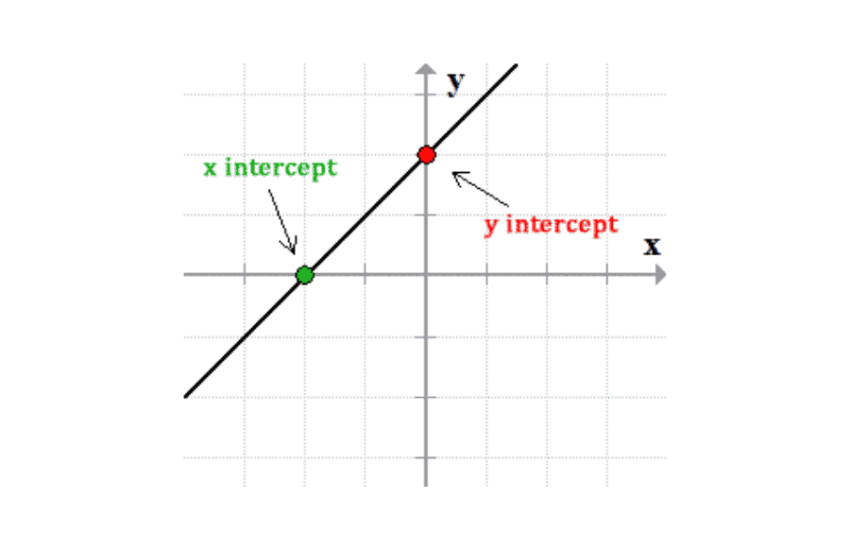
Another effective method for **finding intercepts on a graph** involves plotting the linear equation manually or using graphical tools. By plotting at least two points and drawing a straight line, you can visually identify where the line crosses both the x-axis and the y-axis. This technique is beneficial for visual learners and offers concrete evidence of the relationship in **graphing lines**.
Solving for the Y-Intercept Algebraically
To employ algebraic methods for **solving for the y intercept**, rearranging the equation is necessary. This often entails deriving the constant value of y when x is set to zero. For example, in the standard form Ax + By = C, it can be rewritten as y = (-A/B)x + (C/B), simplifying the calculation of intercepts. This technique aligns effectively with action-based **algebra** and prepares students for broader applications in their studies.
Applications of the Y-Intercept
The applications of the **y-intercept** spread far beyond theoretical calculations in a classroom. Understanding these intercepts can play a significant role in analyzing data across various fields, such as economics, biology, and social sciences, where linear models are commonly used. This peculiarity underlines the importance of the **meaning of y intercept** in real-world scenarios.
Y Intercept in Real Life
In many real-world scenarios, the **y intercept** can indicate starting conditions. For instance, when documenting financial trends, the y-intercept may represent initial investment or revenue at a certain time. Thus, grasping the **applications of y intercept** fosters analytical skills and improves data interpretation capabilities.
Interpreting Graph Intercepts
Once the y-intercept is determined, understanding its implications when graphed is essential. The **significance of y intercept** reflects the initial state of a function before additional variables are introduced. In practical applications, this translates to effective decision-making when analyzing function behavior across various scenarios, potentially impacting outcomes and strategies.
Determining Y Intercept in Systems of Equations
In the context of systems of equations, determining the **y intercept** facilitates the comparative evaluation of multiple datasets. By finding the **y intercepts** of different linear relationships, one can glean insights into their intersections, helping analyze the probability of certain outcomes. This is crucial for sectors like economics and logistics, where precise planning is paramount.
Key Takeaways
- The **y intercept** marks the point where a graph intersects the y-axis, serving critical roles in various mathematical contexts.
- Methods to find the y intercept include the slope-intercept form, graphical representation, and algebraic solutions.
- The **y intercept** holds real-world applications in industries like finance and science, demonstrating its importance beyond theory.
- Interpreting graph intercepts effectively allows for better analysis of trends and behaviors of functions.
- Systems of equations utilize the determination of y intercepts for comparative evaluations and practical outcomes.
FAQ
1. What is the definition of the y intercept?
The **y intercept** is the point at which a line or curve crosses the y-axis on a coordinate graph, representing the value of y when x is zero. It is crucial for comprehending the behavior of linear equations and understanding their graphical representations.
2. How do you calculate the y intercept from an equation?
To **calculate the y intercept**, set the variable x to zero in the function’s equation and solve for y. This value will represent the y-coordinate where the graph intersects the y-axis.
3. Can you give an example of finding the intercepts on a graph?
Yes, for the equation y = 2x + 6, by plotting various points or simply substituting x=0, we find that the y-intercept is 6, meaning the point (0,6) appears on the graph, showing where it crosses the y-axis.
4. Why is the y intercept important in linear functions?
The **y intercept** is important as it provides a starting point for the function, enabling a visual representation of the relationship between x and y. It gives insights into the characteristics of the function, helping in graph interpretations and applications in real life.
5. How is the y intercept relevant to real-world applications?
In real-world applications, especially in economics and science, the **y intercept** can represent initial conditions, such as starting revenues or population sizes. This information is critical for modeling scenarios and making predictions based on trends.
By understanding how to effectively **find the y intercept**, you can enhance your grasp of linear equations and their applications. For continued exploration, refer to this link and here.